In recent years, we have learned that adult brains are more adaptable than previously believed. Studies show that the brain has natural healing properties that allow it to clean and repair damaged cells throughout our lives.
However, there may be things that you are doing (or not doing) which prevent this process from happening.
As a Psychiatrist and Internist, specializing in treatment-resistant depression, I have found that the 10 lifestyle tips below spur holistic healing for depression. Whether you have been diagnosed with depression, or are interested in improving your brain health to help prevent brain diseases such as dementia from developing, these tips can help you improve your mental health naturally.
How the Brain Repairs Damaged Cells
First, let’s take a brief look at how the brain works:
Nerve cells (or neurons) are the main working cells in the brain. These cells allow us to think, move, feel, maintain autonomic activity such as your heartbeat and liver function, and experience memory and emotion.
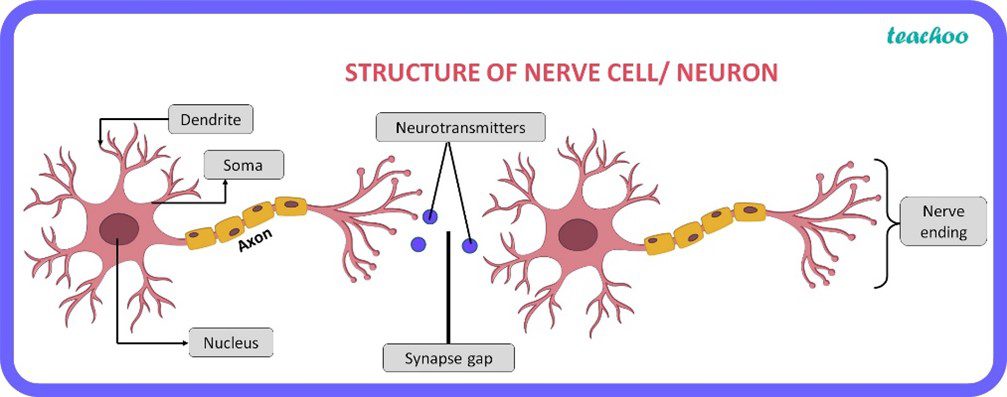
Neuron image from Teachoo, 2023.
An electrical impulse is triggered in the cell body by biochemical information brought to the cell from the dendrites. The impulse then travels along the axon to the nerve ending. At which point the impulse triggers the release of neurotransmitters that cross a gap – the synapse – and are picked up by receptors on the dendrites of the next neuron.
When nerve cells are healthy and robust, we feel better physically and emotionally. Increased neuroplasticity – the ability of neurons to adapt – results in more dendrites and receptors, which allows the brain to work better.
Decreased neuroplasticity can lead to neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease, as well as mental illnesses including depression and anxiety. Brain imaging has shown that aging and neurodegenerative disorders can cause parts of the brain to shrink or develop holes.
Below is a photograph of two brain sections. The one on the left is a healthy brain; the one on the right belonged to a person suffering from Alzheimer’s disease. Note the overall shrinkage, thinning of the cortex (exterior part of the brain), the erosion at the base of the brain, and gaping holes throughout.
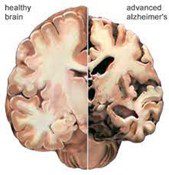
Brain image from ADRC of Southwest Wisconsin, 2019.
Holistic Healing for Depression and Anxiety
The good news is that brain diseases, including mental illnesses, can be decreased, slowed, repaired, and even prevented by simple lifestyle changes. These lifestyle changes improve neuroplasticity, providing natural healing for depression and anxiety.
If you have been diagnosed with depression or anxiety and you are already seeking treatment, these 10 lifestyle tips can be used in conjunction with your mental healthcare plan to improve the effectiveness of your treatment. If you have a more mild case of depression or anxiety, you may be able to use these tips to manage your depression or anxiety without the need for medication or other psychiatric interventions.
However, you do not need a diagnosed mental illness to benefit from these lifestyle tips. As we age, we tend to naturally lose neuroplasticity in the brain. These tips can help you improve neuroplasticity and help your brain function at its best for as long as possible.
10 Lifestyle Tips For Healing Depression Without Medication
Across all mental health conditions, patients who follow these 10 lifestyle recommendations see more dramatic and faster improvements in their mental health.
- No smoking. Smoking causes the brain to age faster. While cognitive decline typically happens naturally as we age, smokers typically experience faster cognitive decline than nonsmokers.
A 2015 research review of 37 studies found that smokers were 30 percent more likely to develop dementia. Fortunately, the review also found that if you quit smoking, your dementia risk eventually decreases to that of a nonsmoker.
- Limit alcohol intake as much as possible. The National Institutes of Health found that “Alcohol interferes with the brain’s communication pathways and can affect the way the brain looks and works.” (nih.gov) Limit your alcohol intake to one drink no more than three times a week.
- Exercise for 30-60 minutes 4-6 days per week. Aerobic activities that sustain an elevated heart rate such as walking, biking, running, or swimming and anaerobic activities like lifting weights and resistance training are all beneficial for the brain.
Exercise increases a hormone in your brain called brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) which helps your brain grow and promotes neuroplasticity. BDNF can offset the natural aging process. Read how to stick to an exercise routine.
- Minimize consumption of processed sugar. High sugar consumption can lead to metabolic syndrome, which can develop into Type 2 Diabetes. Both of these conditions can cause brain atrophy.
The National Institutes of Health reported that one-third of American adults have metabolic syndrome. And, those with metabolic syndrome are twice as likely to develop dementia.
Reduce your intake of granulated sugar, high fructose corn syrup, honey, maple syrup, and fruit juices.
Compare food labels and choose items with the lowest amount of added sugars.
– Choose whole fruits and vegetables over packaged snacks.
– Drinking water or unsweetened iced tea instead of soda. - Limit your consumption of grain products (especially processed wheat). Wheat, like sugars, can cause a spike in blood sugar that can reduce neuroplasticity and lead to brain atrophy.
Consuming grain products can also make your gut more permeable. This allows proteins that are too large into your bloodstream and causes an immune response that attacks other parts of your body. This can result in arthritis, autoimmune diseases, and damage to your brain.
- Sleep 8 hours per night. Sleep is when the brain cleans itself. The glymphatic system is a group of structures and processes that allow the brain to clear out soluble waste products. It operates mainly during sleep, and unfortunately, there are no other ways to trigger this process.
If you have trouble sleeping, taking 0.5-3 mg of melatonin can help. Instead of using other sleep aids, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention offers these suggestions:
– Follow a consistent sleep schedule every day – going to be and waking up at the same time – including weekends.
– Make sure your bedroom is quiet, dark, relaxing, and at a comfortable temperature. For some people, this may mean investing in black-out curtains, a fan, or ear plugs.
– Remove electronics from your bedroom.
– Avoid large meals, caffeine, and alcohol before bedtime.
– Get some exercise. Being physically active during the day can help you fall asleep more easily at night.
– Treat sleep apnea. - Take vitamin D3 supplements. At our clinic, we perform laboratory testing to see if there are vitamins or minerals that our patients may be lacking. Most people living in North America have less than optimal vitamin D levels.
Once on Vitamin D supplements, a blood level should be checked. There are few dangers associated with having high levels of vitamin D.Vitamin D has been shown to:
– Reduce inflammation
– Reduce auto-immunity
– Improve brain function
– Reduce cancer cell growth
– Improve immunity
– Improve mood and sleep
– Reduce risk of heart disease - Take fish oil pills. Omega-3 fatty acids are abundant in the cell membranes of brain cells, preserving cell membrane health and facilitating communication between brain cells.
The hippocampus interacts with millions of neurons to regulate learning, encode and consolidate memories, and retrieve memories to form cognitive maps that aid in spatial navigation. This very complex organ shrinks with age. Omega-3 supplementation reduces shrinkage and encourages robust interaction between the hippocampus and neurons (MSUToday).
Start with a low dosage, and work up to 2,000 mg twice per day. There are two kinds of omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil: EPA & DHA. Look for a supplement that has a high EPA percentage. - Fast 12 hours between dinner and breakfast each day. When you are no longer using food or sugar to produce energy, the process of autophagy takes over. Autophagy breaks down old cells, allowing your body to replace them with new cells that function more efficiently.
Fasting can increase brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), the hormone that makes your brain grow and promotes neuroplasticity.
- Challenge your brain! Learning something new and challenging your brain creates new synaptic connections and promotes neuroplasticity. Here are some examples you can try:
– Meditation
– Devote time to mentoring, tutoring, or coaching a sport
– Join a book club, art club, or other social group
– Read a challenging book
– Learn a new language
– Play a musical instrument, one you played long ago or try a new one
– Learn a new card game or board game
– Volunteer at a local nonprofit or library
– Take a class for a new hobby such as woodworking or cookingBrain scans and cognitive tests taken a year after learning a challenging new skill (like photography) demonstrate significantly better cognitive performance. The more intellectual stimulation you have, the more neural circuits you use. Elise Caccappolo, Ph.D. in neuropsychology at Columbia University Medical Center, states, “The more circuits you have, the harder it is for neurodegenerative diseases to manifest.” (6 Tips to Maximize Brain Health)
Check out some of these books for more ways to improve your brain health and heal depression and anxiety holistically:
Bredesen, Dale E. The End of Alzheimer’s: The First Program to Prevent and Reverse Cognitive Decline. (2017.) Avery, a division of Penguin Publishing Group.
Mosconi, Lisa. Brain Food: The Surprising Science of Eating for Cognitive Power. (2019.) Avery, a division of Penguin Publishing Group.
Null, Gary. Reboot Your Brain: Diet and Lifestyle Techniques to Improve Your Memory and Ward Off Disease. (2015.) Skyhorse.
Perlmutter, David. Grain Brain: The Surprising truth about Wheat, Carbs, and Sugar – Your Brain’s Silent Killers. (2018.) Little, Brown, Spark.

Stephen Manlove, MD graduated from the University of Minnesota Medical School and completed residencies in Psychiatry and Internal Medicine through the University of Virginia Medical School. He holds multiple board certifications in psychiatry/neurology, internal medicine and forensic psychiatry. This deep understanding of medicine gives him a unique ability to practice truly holistic psychiatry—fusing lifestyle changes and brain health best practices with genetic testing and a detailed laboratory workup to develop a personalized plan for each patient. As an early adopter of transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and ketamine/Spravato, he and the Advanced Brain + Body team have helped thousands of patients suffering from treatment resistant depression, anxiety and PTSD.

